[ad_1]
NVIDIA and UC San Diego researchers have created AnyTeleop, a pc vision-powered teleoperation system for numerous purposes.
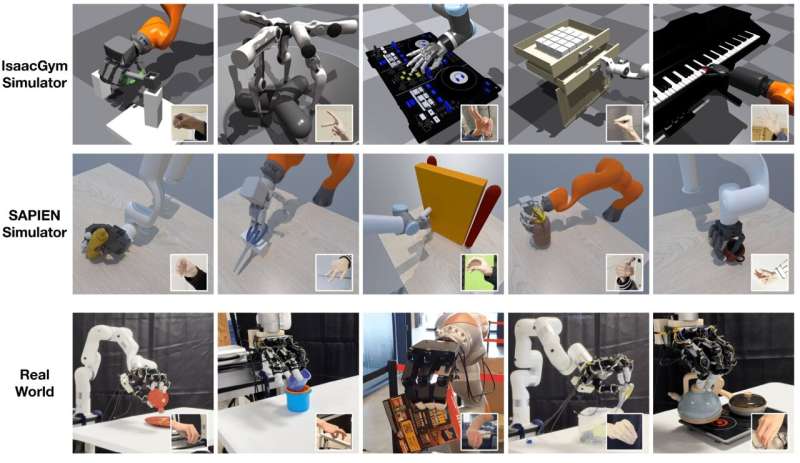
Latest breakthroughs in robotics and synthetic intelligence (AI) have expanded teleoperation potentialities, permitting distant duties like museum excursions or upkeep in inaccessible areas. Nonetheless, most teleoperation programs are designed for particular settings and robots, limiting their broad adaptability.
Researchers at NVIDIA and UC San Diego have developed AnyTeleop, a teleoperation system pushed by pc imaginative and prescient designed for broader utility eventualities. Prior analysis emphasised how a human teleoperates or directs the robotic. Nonetheless, this technique faces two challenges. Initially, coaching a top-tier mannequin calls for quite a few demonstrations. Furthermore, the configurations typically contain costly gear or sensory {hardware} tailor-made solely for a selected robotic or deployment setting.
The crew aimed to develop an inexpensive, easy teleoperation system, and versatile throughout varied duties, settings, and robots. To hone their system, they managed digital robots in simulations and actual robots in bodily settings, minimizing the need to purchase and construct quite a few robots. By way of single or a number of cameras, the system screens human hand positions and adapts these to information the actions of a robotic hand with a number of fingers. The wrist’s place drives the robotic arm’s motion, facilitated by a CUDA-driven movement planner.
Not like many earlier teleoperation programs, AnyTeleop boasts versatility, suitable with varied robotic arms, palms, digicam setups, and simulated and real-world environments. It’s appropriate for each close-range and distant consumer eventualities. Moreover, the AnyTeleop platform assists in gathering human demonstration information, which captures the nuances of human actions throughout particular duties. This invaluable information can improve the coaching of robots to carry out duties autonomously. In preliminary trials, AnyTeleop surpassed the efficiency of a specialised teleoperation system, even when used on the robotic it was designed for. This underscores its potential to raise teleoperation makes use of.
NVIDIA plans to launch an open-source variant of AnyTeleop, enabling world analysis groups to experiment with and adapt it for his or her robots. This rising platform holds the potential to amplify teleoperation system deployment and support in gathering coaching information for robotic manipulators.
Reference: Yuzhe Qin et al, AnyTeleop: A Common Imaginative and prescient-Primarily based Dexterous Robotic Arm-Hand Teleoperation System, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2307.04577
[ad_2]
