[ad_1]
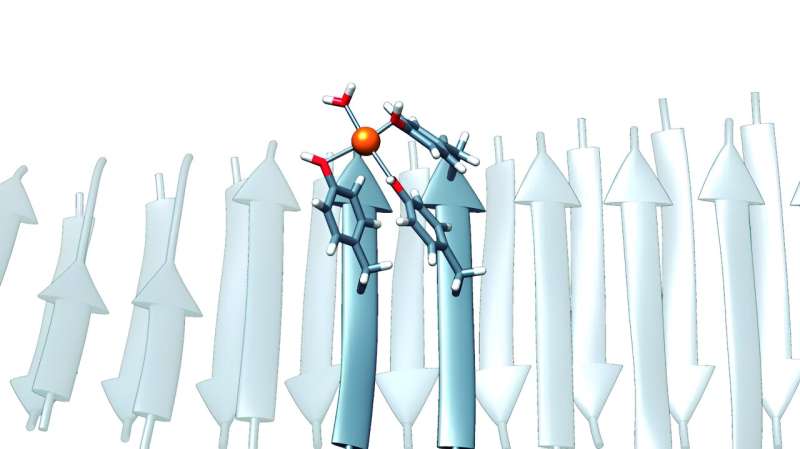
Autonomous College of Barcelona (UAB) researchers have developed minimal nanozymes with the capability of capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emitted in industrial processes—and relevant to different environmental remediation processes—primarily based on synthetic molecular buildings fashioned by the peptides of solely seven amino acids.
These new molecules may additionally act as metalloenzymes, and this opens up new potentialities in biotechnology analysis. The research additionally supplies a brand new contribution to the origin of catalytic exercise in the beginning of life.
The analysis, with Salvador Ventura as coordinator and Susanna Navarro as first creator, was just lately printed in ACS Nano. Each are researchers on the Institute of Biotechnology and Biomedicine and on the UAB Division of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and have labored collectively within the research with researchers from the UAB Division of Chemistry and the Analysis Middle bioGUNE.
In 2018, UAB researchers managed to create very quick molecules able to self-assembly, impressed by the pure skill to self-assemble of amyloid fibrils, and primarily based on a selected sequencing of prion proteins. These synthetic amyloids have catalytic actions, with benefits similar to modularity, flexibility, stability and reutilisation when in comparison with pure enzymes.
Now, researchers have found their capability to bind to steel ions successfully and act as steel and metalloenzyme-storage components.
“These peptides have been explicit, since they didn’t comprise the everyday amino acids, similar to histidine, which is usually thought-about important for the coordination of steel ions in enzymes, and which have been considered important for catalytic exercise. In distinction, they have been enriched with residues from tyrosine, a component which though much less identified on this context, also can have the distinctive capability of binding to steel ions if it finds itself within the right structural context. Tyrosine’s skill to take action is what we used to create our nanozymes,” Ventura stated.
The outcomes will be utilized to a number of areas. First, nanozymes are steady and can be utilized for environmental remediation, in wastewater therapy processes or contaminated soils, given their notable capability for sequestrating steel ions.
Second, they’ll perform as metalloenzymes, able to catalyzing reactions in situations during which present enzymes, a lot much less steady, can be incapable of performing. This opens up new potentialities in analysis into biotechnology, similar to in catalyzing reactions in excessive temperatures and pH values.
Based mostly on the nanozymes they designed, researchers are satisfied that they’ve efficiently developed a minimalistic variant of a carbonic anhydrase enzyme able to effectively storing CO2 emitted by greenhouse gases, and at a a lot decrease manufacturing price than pure enzymes.
New perspective on ancestral enzymes
To acquire these new nanozymes, researchers fashioned the speculation that catalytic exercise on the origin of life may have emerged as the results of the self-assembling of quick, low-complexity peptides into buildings just like amyloids which acted because the primal ancestral enzymes.
“Exhibiting that these molecules have catalytic motion with out the necessity of typical histidine-based coordination represents a major change in how we perceive the origin of catalytic exercise initially of life. We now know that this exercise will be achieved if the ancestral peptides comprise tyrosine. Due to this fact, we propose that it’s extremely possible that the ancestral enzymes primarily based on amyloids additionally used this second amino acid of their chemical reactions,” Ventura concludes.
Within the research, researchers mixed experiments and simulations through the use of a wide range of methods similar to spectrophotometry, flourescence, electron microscopy, electron diffraction, and superior computational modeling.
Extra data:
Susanna Navarro et al, Amyloid Fibrils Shaped by Quick Prion-Impressed Peptides Are Metalloenzymes, ACS Nano (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c04164
Offered by
Autonomous College of Barcelona
Quotation:
Researchers develop minimal nanozymes with carbon dioxide seize capability (2023, September 26)
retrieved 30 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-minimal-nanozymes-carbon-dioxide-capture.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.
[ad_2]
