[ad_1]
They’re used as medicines, drug carriers and to fight microbes in hospitals, destroy plant pathogens and cut back the quantity of conventional fertilizers utilized in agriculture—nanoparticles are taking up medication and the agri-food business.
Nanoparticles are tiny buildings as much as 100 nanometers in dimension. They’re characterised by completely different bodily and chemical properties and organic exercise than their bigger materials counterparts.
“When the beginning materials on a micro-scale with a selected floor space is damaged right down to nano dimension, i.e. into smaller particles, its floor space will enhance many occasions. And it’s the ratio of floor to quantity that ends in the distinctive properties of nanoparticles,” explains Prof. Mahendra Rai from Sant Gadge Baba Amravati College in India.
Nanoparticles may be primarily natural or inorganic. Among the many natural ones, we are able to distinguish liposomes, micelles, and dendrimers.
“Liposomes are vesicles product of a phospholipid bilayer with free area inside, in which you’ll be able to put, for instance, a drug and exactly ship it to the goal place within the physique as a result of the liposomes will disintegrate within the acidic setting of the tumor and launch the drug in it,” says, prof. Patrycja Golinska from the Division of Microbiology on the School of Organic and Veterinary Sciences NCU.
“Amongst inorganic nanoparticles, we are able to distinguish nanoparticles of metals reminiscent of silver, gold, titanium, copper, steel oxides (e.g. zinc oxide) and semi-metals (metalloids) reminiscent of silica, selenium, and aluminum. At Nicolaus Copernicus College, we targeted primarily on steel nanoparticles. To date, we have now largely biosynthesized silver and gold nanoparticles. Lately, we have now additionally biosynthesized nanoparticles of zinc, copper, and magnesium oxides.”
Nanoparticles may be obtained in numerous methods, however lately, the so-called inexperienced synthesis (organic synthesis or biosynthesis) has attracted growing curiosity in nanotechnology.
“It’s environmentally pleasant. In organic synthesis, not like chemical or bodily synthesis, the manufacturing of nanoparticles doesn’t use poisonous compounds and doesn’t devour giant quantities of power”, says Prof. Rai.
As well as, after the manufacturing of nanoparticles in a chemical or bodily approach, they nonetheless must be stabilized, i.e. “coated” with different chemical compounds, that are often additionally poisonous. The purpose is that the nanoparticles don’t mixture, i.e. don’t mix with one another into buildings of bigger sizes and don’t lose their response floor and thus their distinctive properties.
Inexperienced nanotechnology
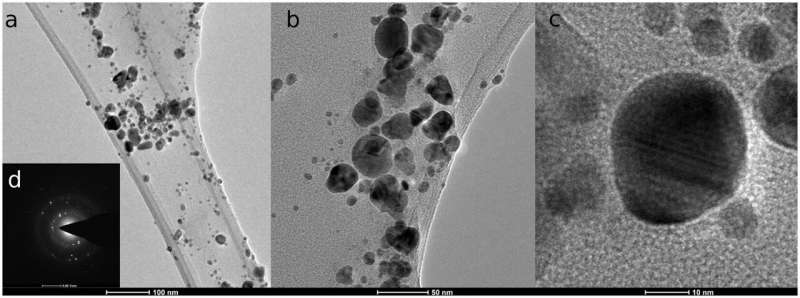
Biologists from the Nicolaus Copernicus College in Toruń grew to become all for biosynthesis, i.e. the synthesis of nanoparticles by microorganisms reminiscent of fungi and micro organism, in addition to by algae and vegetation. Throughout the go to of Prof. Rai in Poland, scientists targeted on mycosynthesis, i.e. the synthesis of nanoparticles utilizing fungi.
“As a part of the mission, which Prof. Rai carried out on the Nicolaus Copernicus College, we synthesized silver nanoparticles utilizing fungi, primarily of the genus Fusarium, which infect vegetation, together with cereals, but in addition from different genera like Penicillium, which develop e.g. on tangerines and lemons,” says prof. Golinska. “In such manufacturing, no poisonous compounds are used and no poisonous waste is produced.”
The benefit of fungi over different microorganisms within the synthesis of nanoparticles is that they produce numerous numerous metabolites, together with many proteins, together with enzymes, and lots of of those substances may be concerned within the discount of silver ions to nanosilver.
Functions
Nanotechnology can be utilized in a very powerful areas of human life: medication, agriculture and the packaging business, and meals storage. Nanoparticles are extremely lively towards numerous microorganisms.
They combat pathogenic microbes very nicely and inhibit their unfold, which can be utilized to supply numerous surfaces and supplies in hospitals, reminiscent of masks with a nanosilver filter, which have been created through the COVID-19 pandemic. They’re efficient towards micro organism which can be immune to generally used antibiotics. Silver nanoparticles even have anti-cancer properties.
“Nanomaterials are good, they are often administered, for instance, intravenously, however they work on the goal website, i.e. in a cancerous tumor, and never like chemotherapy, which is distributed all through the physique on the identical time destroying each irregular and wholesome cells,” explains Prof. Rai. Within the case of nanoparticles, we are able to use focused remedy, by which the anti-cancer drug will probably be launched solely on the website of the tumor. Nanoparticles themselves is usually a drug, and likewise a drug provider.
In agriculture, nanotechnology is utilized in three elements. The primary is the early detection of plant pathogens earlier than the primary signs of plant illness seem. The digital nostril is a know-how that we don’t take care of in the intervening time, however due to using nanomaterials reminiscent of nanowires or nanorods of zinc oxide on this gadget, it detects unstable substances produced by pathogenic fungi.
“Different varieties of nanobiosensors detecting the DNA of plant pathogens can be used,” says Prof. Golinska. “Because of this, acceptable agrotechnical remedies may be utilized earlier than we see the signs of plant infestation, e.g. discoloration, raids or necrosis of leaf blades.”
The second side is using an answer of nanoparticles to immediately fight pathogens which have already developed on vegetation. Such nanoparticles often act at a lot decrease concentrations than chemical fungicides, so their focus within the setting can also be a lot decrease in comparison with generally used fungicides.
The third space of software of nanomaterials in agriculture is the supply of vitamins to vegetation. As in medication, nanomaterials themselves is usually a nutrient or a provider containing a nutrient that may be launched in a managed method. When farmers use conventional fertilizers, they ship an enormous quantities of them to the fields in a short while, which vegetation are unable to make use of and a big a part of them penetrates deep into the soil to groundwater and, consequently, to water reservoirs (floor water).
This adversely impacts the aquatic setting resulting in its eutrophication. Extreme fertilization additionally harms soil microorganisms and results in the so-called. “Soil fatigue,” i.e. a relentless imbalance within the content material of vitamins, which negatively impacts the dimensions of crops. Utilizing nanoencapsulation, i.e. inserting nanoparticles which can be vitamins for vegetation in capsules or matrices, you possibly can apply these vitamins by foliar or soil software.
“The most important benefit of this resolution is the discharge of vitamins in a managed, sluggish and fixed approach. This is a component of sustainable improvement, which is extraordinarily necessary these days,” says Prof. Rai.
Pleasant fungi
Prof. Rai got here to Poland for 2 years due to a scholarship he obtained from the Polish Nationwide Company for Educational Change (NAWA). Underneath the proposed mission, “Improvement of recent environmentally-friendly and biologically lively nanomaterials” along with a staff consisting of Dr. hab. Patrycja Golińska (prof. of NCU), Dr. Magdalena Wypij, and Ph.D. scholar Joanna Trzcińska-Wencel, handled the manufacturing of nanocomposites based mostly on pullulan and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) for combating numerous microorganisms.
“Pullulan, a pure biodegradable polymer, was biosynthesized utilizing fungi (Aureobasidium pullulans) and mixed with silver nanoparticles, produced by inexperienced synthesis utilizing mildew fungi, which I discussed earlier,” explains Prof. Golińska. “We created movies, i.e. skinny and versatile foils, encrusted with silver nanoparticles. We examined these movies, for instance, to fight pathogens liable for wound infections or people who develop in meals, reminiscent of Listeria monocytogenes or Salmonella sp., i.e. de facto to increase the shelf lifetime of meals.”
Pullulan integrated with silver nanoparticles presents useful properties and subsequently could possibly be used, for instance, within the manufacturing of meals packaging or dressings which speed up the therapeutic of wounds, defending them towards the event of an infection. “When we have now extra in depth wounds, e.g. burns, they’re extremely uncovered to the event of an infection,” explains Prof. Golińska. “Securing such a spot with a biodegradable polymer with an agent inhibiting the event of pathogens will considerably speed up wound therapeutic.”
The staff intends to patent a technique for acquiring pullulan-based nanocomposites and releasing nanoparticles from the movie.
Two analysis papers have been revealed within the journal Frontiers in Microbiology through the professor’s go to, specifically “Biogenic nanosilver bearing antimicrobial and antibiofilm actions and its potential for software in agriculture and business” and “Superior in vivo wound-healing exercise of mycosynthesized silver nanogel on completely different wound fashions in rat.”
One other two, “Biofabrication of novel silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles from Fusarium solani IOR 825 and their potential software in agriculture as biocontrol brokers of phytopathogens, and seed germination and seedling development promoters” and “Pullulan-based movies impregnated with silver nanoparticles from Fusarium culmorum pressure JTW1 for potential functions in meals business and medication” have been revealed simply after Prof. Rai left Poland. The papers have been revealed in Frontiers in Chemistry and Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.
Extra info:
Joanna Trzcińska-Wencel et al, Biogenic nanosilver bearing antimicrobial and antibiofilm actions and its potential for software in agriculture and business, Frontiers in Microbiology (2023). DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1125685
Swapnil Gaikwad et al, Superior in vivo Wound-Therapeutic Exercise of Mycosynthesized Silver Nanogel on Completely different Wound Fashions in Rat, Frontiers in Microbiology (2022). DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.881404
Joanna Trzcińska-Wencel et al, Biofabrication of novel silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles from Fusarium solani IOR 825 and their potential software in agriculture as biocontrol brokers of phytopathogens, and seed germination and seedling development promoters, Frontiers in Chemistry (2023). DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1235437
Magdalena Wypij et al, Pullulan-based movies impregnated with silver nanoparticles from the Fusarium culmorum pressure JTW1 for potential functions within the meals business and medication, Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1241739
Offered by
Nicolaus Copernicus College
Quotation:
Synthesis of nanoparticles by microorganisms: Exploring the inexperienced energy of fungi (2023, September 8)
retrieved 9 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-synthesis-nanoparticles-microorganisms-exploring-green.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
[ad_2]
